- Many ship waste systems allow hazardous food waste into sewage and greywater.
- This gives rise to biosecurity threats and to be safely disposed of.
- Non-compliant waste disposal systems are being approved by maritime authorities and class societies.
- Food waste can spread plant pests, as well as livestock and poultry diseases (swine flu).
- Many countries have strict biosecurity regulations while others have ad-hoc measures.
- Annex V of IMO’s MARPOL Convention permits three routes for a ship’s food waste.
- It includes to the sea; to an onboard incinerator; and to port reception facilities.
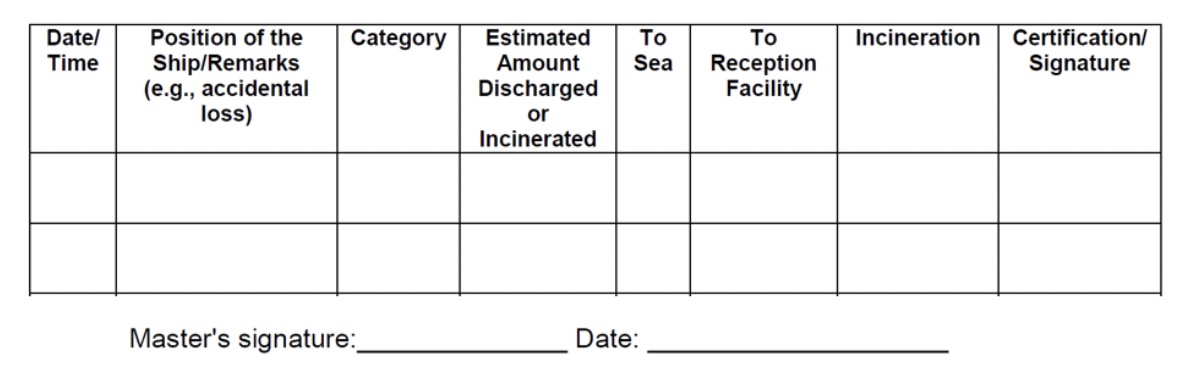
- The actual disposal route must be recorded in a Garbage Record Book.
According to an article published in Splash247, many ship waste systems allow potentially hazardous food waste to disappear into sewage and greywater.
Biosecurity threats
IMO and national laws on biosecurity which legislate for the separation and safe disposal of food waste. There have not been any prosecutions yet but the fall-out of the current pandemic means ramped up efforts on biosecurity are likely reports Dr. Wen Chei from Wärtsilä.
Waste disposal on some vessels contravenes both maritime and national biosecurity legislation by allowing food waste into greywater systems. From there, food waste that is meant to be separated and carefully disposed of disappears when ships discharge sewage and greywater. The result is that the local community and environment are exposed to potential biohazards, ship owners to legal prosecution and maritime authorities to charges of weak compliance and enforcement.
Non-compliant waste disposal systems pose a threat
The fact that non-compliant waste disposal systems are being approved by maritime authorities and their recognized organizations (including class societies) should cause grave concern. A legal system would be deemed a failure if a prisoner could simply run away. In this case, the prisoner can even stop and say hello as he walks past the guard.
The COVID-19 pandemic highlights that biosecurity has never been more important. Although the coronavirus is not passed through food waste, one does not have to look back too far to find examples of diseases that can be transmitted through food. Last year, for example, an outbreak of African swine flu put pig populations in Asian countries at risk [1].
National legislation
Food waste can spread plant pests, as well as livestock and poultry diseases such as swine fever, rabies, foot and mouth disease or avian flu. Some countries have strict biosecurity regulations falling under the jurisdiction of the national agricultural authorities, while others have ad-hoc measures.
- In Europe, food waste that is ‘international catering waste’ is classed as Category 1 material, carrying the highest level of risk. It must be stored and transported in covered and leakproof containers to approved incineration facilities or landfills for deep burial.
- In US territorial waters, food waste on or removed from a ship is ‘regulated garbage’ if the ship has been in any port outside the US and Canada in the last two years. It must be stored in tight, leakproof covered containers and taken to approved facilities for incineration, sterilization, or disposal in an approved sewage system.
- In Canada, food waste (or ‘ship’s refuse’) from outside Canada and the US is to be stored in closed leakproof containers and removed at the first port of entry to approved facilities for incineration or sterilization, or landfills for deep burial.
- Australia considers international food waste a biosecurity risk and has requirements for the collection, storage, and transport of this waste for acceptable disposal methods.
- In New Zealand, food waste is categorized as ‘risk goods’. While within New Zealand territorial waters, risk goods (other than for biosecurity clearance at a place of the. first arrival) shall be secured onboard the vessel. This includes being kept in a leakproof, vermin-, insect- and bird-proof container or room.
In brief, these rules demand that food waste be either discharged to the sea beyond 3 nm or 12 nm from the nearest land, or transferred to the approved facilities for disposal. In the meantime, it must be managed in a way that is leakproof.
International regulation
Annex V of IMO’s MARPOL Convention permits three routes for a ship’s food waste: to the sea (beyond 3 or 12 nm from the nearest land); to an onboard incinerator; and to port reception facilities. The actual disposal route must be recorded in a Garbage Record Book.
However, the convention itself never makes any reference to biosecurity. Some requirements related to biosecurity risks exist only in Guideline MEPC.295(71), which states in section 2.9.2 that food waste should be directed into an appropriately constructed holding tank when discharge is prohibited. It also states that food waste carrying a risk of diseases or pests should be kept separately and stored in clearly marked and tightly covered containers, and preferably retained for discharge at port reception facilities in accordance with the laws of the receiving country.
Importantly, the IMO’s Survey Guideline, Resolution A.1120(30), has no survey requirements to food waste-related scopes under MARPOL Annex V – let alone those related to the biosecurity rules of national agricultural authorities. Even where national inspection regimes on biosecurity rules are in place, they have not been effective enough in spotting or stopping non-compliance.
Realities
On many ships, food waste and its derivatives are sent, in whole or in part, to the greywater system, where it vanishes without a trace. Such practices have been documented in various reports, sometimes commissioned by the maritime authorities. The technical standards of some classification societies permit food waste to be sent to the sewage treatment plant instead of a food waste food holding tank as stipulated in section 2.9.2 of MEPC.259(71). Such standards create non-conformity because the sewage treatment plant is not one of the three permitted routes in the Garbage Record Book, which is completed and signed by the ship Master.
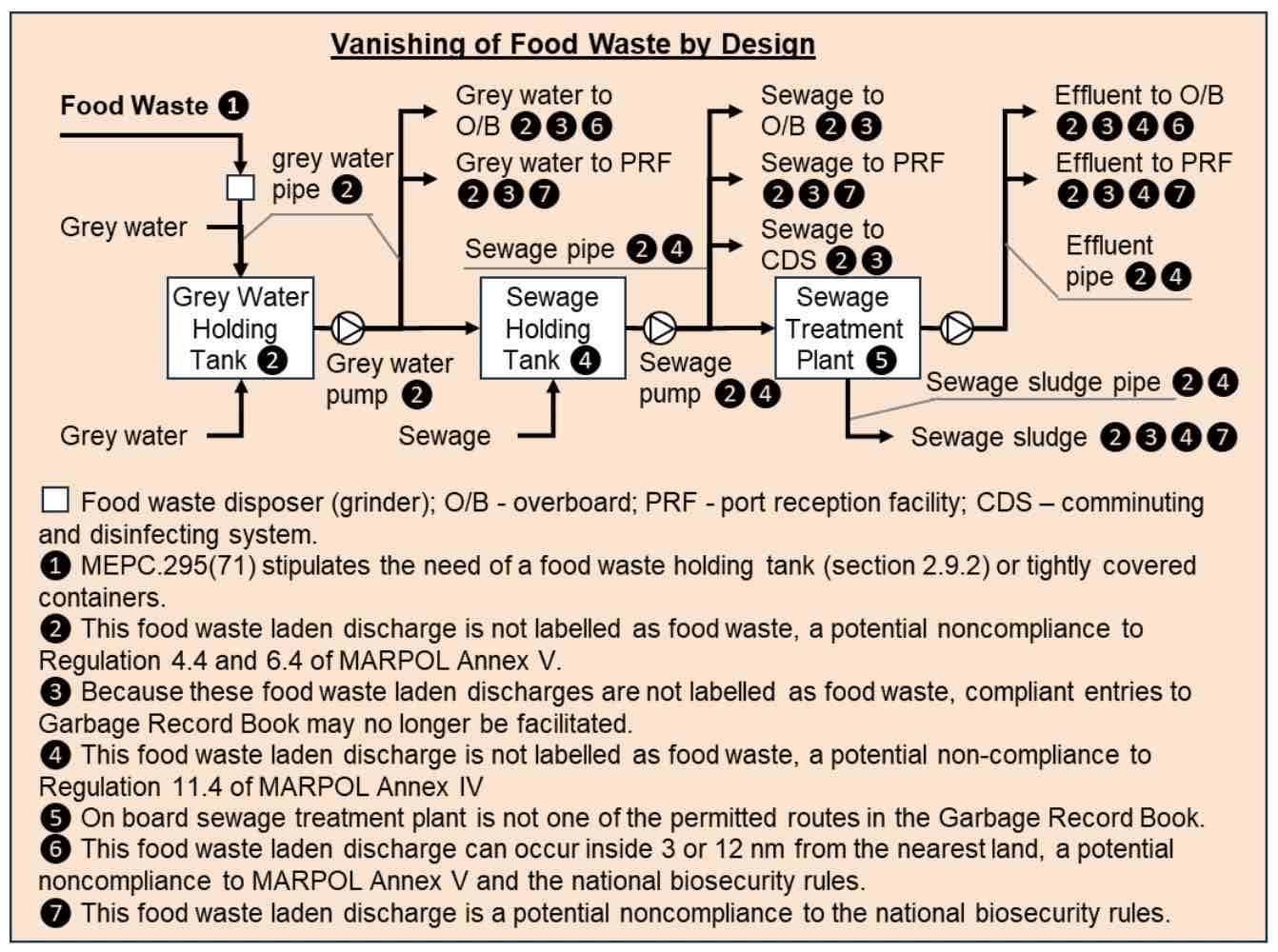
Threats due to non-compliances
The diagram below illustrates the extent of potential non-compliances, looking at a food waste disposer as one of many potential examples. Food waste entering the system from the top left corner of the diagram never comes out from the system; it simply vanishes. Tracing the lines to the port reception facilities (PRF), it is clear how food waste gets ashore in disguise, escaping the ‘approved facilities’ intended by the local biosecurity rules. From there it can end up on the agricultural land, carrying biosecurity risks with it.
 The contrast between the aviation industry and the marine industry can be startling. It is evident that the global aviation industry follows the rules by the book (and possibly through gritted teeth). One airport even built its own incinerator to dispose of food waste responsibly. While one industry builds waste incinerators, the other fits food waste grinders instead.
The contrast between the aviation industry and the marine industry can be startling. It is evident that the global aviation industry follows the rules by the book (and possibly through gritted teeth). One airport even built its own incinerator to dispose of food waste responsibly. While one industry builds waste incinerators, the other fits food waste grinders instead.
Conclusion
Let us hope that maritime and agricultural authorities interpret and enforce their biosecurity rules consistently. Until then, it will be business as usual for improper practices to spread on ships – both by design and by approval.
Did you subscribe to our daily newsletter?
It’s Free! Click here to Subscribe!
Source: Splash247















